General Information about Solian
In addition to medicine, remedy and support from mental health professionals are important in managing schizophrenia and other psychiatric disorders. Solian is best when utilized in mixture with a comprehensive treatment plan that features therapy, assist teams, and life-style changes.
The active ingredient in Solian is amisulpride, which works by blocking the neurotransmitter dopamine within the mind. Dopamine is a chemical messenger that plays a role in regulating feelings, motion, and cognition. An imbalance in dopamine ranges has been linked to schizophrenia and other psychological health disorders.
Solian is a extensively used and effective medication for the therapy of schizophrenia and other psychological well being issues. It helps alleviate symptoms and improve the standard of life for sufferers. However, it may be very important perceive that this treatment may not work for everybody and is probably not the most fitted choice for sure individuals.
Solian just isn't really helpful to be used in children and adolescents beneath the age of 18, as its safety and efficacy in this age group haven't been established. Pregnant and breastfeeding girls should also consult with their physician earlier than taking this medication.
In some uncommon cases, Solian might trigger more severe unwanted effects similar to fainting, irregular heartbeat, or an allergic reaction. If any of those happen, medical attention should be sought immediately.
As with any antipsychotic medication, Solian should not be stopped abruptly with out the steering of a health care provider. Suddenly stopping the medication could cause withdrawal symptoms, similar to nausea, vomiting, and anxiety. It is essential to gradually scale back the dosage under medical supervision.
The most typical side effects reported with Solian are nausea, dizziness, constipation, dry mouth, and anxiety. These normally improve over time as the body adjusts to the medication. However, if these unwanted aspect effects persist or become bothersome, it may be very important converse with a physician.
In conclusion, Solian is a priceless medication within the therapy of schizophrenia and other psychiatric issues. Its unique mechanism of action, along with its decrease risk of side effects, makes it a most popular selection for lots of healthcare professionals. However, it is essential to use this medicine with caution and to hunt steering from a health care provider if any issues come up.
It can also be essential to note that whereas Solian might help handle signs, it isn't a cure for schizophrenia. It is necessary for individuals to proceed taking the medication as prescribed and to attend therapy and support sessions frequently.
One of the main advantages of Solian over traditional antipsychotics is that it has a lower danger of causing unwanted facet effects such as weight achieve and motion disorders. This is as a outcome of it particularly targets dopamine levels within the mind, unlike older antipsychotics that may affect different neurotransmitters as nicely. However, as with any treatment, there is a risk of experiencing some unwanted side effects.
Solian is a medicine used to treat schizophrenia and different psychiatric problems. It is classified as an atypical antipsychotic, meaning it really works in another way from traditional antipsychotics. This medication is especially prescribed to manage symptoms similar to hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized considering.
Solian is available in tablet kind and is often taken a few times a day, depending on the severity of the situation. The dosage is set by a healthcare skilled and will range amongst individuals. It is essential to comply with the prescribed dosage and to not cease or change the treatment with out consulting a physician.
Higher doses of lenalidomide are associated with unacceptable toxicity including life-threatening tumor flare in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia symptoms 7 days before period 100 mg solian amex. Tumor lysis syndrome/tumor flare reaction in lenalidomide-treated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Final results of a multicenter phase 1 study of lenalidomide in patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Lenalidomide as initial therapy of elderly patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Single-agent lenalidomide in the treatment of previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia. The myeloma drug lenalidomide promotes the cereblon-dependent destruction of Ikaros proteins. Bendamustine + rituximab chemoimmunotherapy and maintenance lenalidomide in relapsed, refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma: a Wisconsin Oncology Network Study. Allogeneic related donor hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and the International Bone Marrow Transplant Registry. Transplantlite: induction of graft-versus-malignancy using fludarabine-based nonablative chemotherapy and allogeneic blood progenitor-cell transplantation as treatment for lymphoid malignancies. Evidence of a graft-versus-leukemia effect in chronic lymphocytic leukemia after reduced-intensity conditioning and allogeneic stem-cell transplantation: the Cooperative German Transplant Study Group. Predictors of improved progression-free survival after nonmyeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation for advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Fiveyear follow-up of patients with advanced chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation after nonmyeloablative conditioning. Clinical practice recommendations for use of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia on behalf of the guidelines committee of the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. The genetics of Richter syndrome reveals disease heterogeneity and predicts survival after transformation. Glucocorticoid binding and cytolethal responsiveness of hairy-cell and chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Rituximab in combination with high-dose methylprednisolone for the treatment of fludarabine refractory highrisk chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Methylprednisolone-rituximab is an effective salvage therapy for patients with relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia including those with unfavorable cytogenetic features. Dosedense high-dose methylprednisolone and rituximab in the treatment of relapsed or refractory high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Rituximab in combination with high-dose dexamethasone for the treatment of relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Classic hairy cell leukemia is a rare chronic B-cell lymphoproliferative disorder with unique morphologic features and an excellent prognosis. Bouroncle and colleagues described 26 patients in 1958 with what then was called "leukemic reticuloendotheliosis" and are credited with the initial description of hairy cell leukemia as a distinct clinical entity. Splenectomy was the first effective treatment described and remained the therapeutic modality of choice for many years. Although the mechanism of benefit is not clear, removing the spleen leads to normalization of the peripheral blood counts in approximately one-half of all patients. In the United States, hairy cell leukemia represents 2% of adult leukemias, with only approximately 600 to 800 new cases diagnosed each year. An association with exposure to benzene,54,55 organophosphorus insecticides,56 or other solvents57 has been suggested but has not been confirmed. Circulating hairy cells are often present in the peripheral blood but may be difficult to detect. The initial evaluation should include a history and physical examination, a complete blood count with differential count, review of the peripheral blood smear, measurement of routine serum electrolytes, blood urea nitrogen and creatinine determination, assay of hepatic transaminases, bone marrow aspiration and core biopsy, and immunophenotyping by flow cytometry of peripheral blood or bone marrow aspirate. At the time of diagnosis, patients may have symptoms attributable to anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, or splenomegaly. Approximately 25% of patients have fatigue or weakness and 25% have infection; another 25% come to medical attention because of incidental discovery of splenomegaly or an abnormal peripheral blood count. The most common and invariably the only physical finding is splenomegaly, occurring in approximately 80% of patients. Unlike in many other chronic lymphoproliferative disorders, peripheral adenopathy is uncommon at diagnosis, with less than 10% of patients having peripheral nodes larger than 2 cm. Although adenopathy is not common at diagnosis, internal adenopathy may develop after a prolonged disease course78,79 and is present in 75% of patients at autopsy. The nuclei of the hairy cells are eccentrically located and exhibit a reticular chromatin. The cytoplasm is abundant, and the cytoplasmic borders are irregular, with fine, hairlike projections. The hairy cell nuclei are widely spaced, separated from one another by a pale, lightly eosinophilic cytoplasm. Leukocytosis at presentation is particularly common among those with hairy cell leukemia variant. Hairy cells can be identified in Wright-stained blood smears from almost all patients with hairy cell leukemia, although the number of circulating hairy cells usually is low. The neoplastic cells are approximately one to two times the size of a small lymphocyte.
Home allergen monitoring and controlimproving clinical practice and patient benefits medications by class cheap solian online visa. Fundamentals of Mold Growth in Indoor Environments and Strategies for Healthy Living. Comparison of pollen sampling with a Burkard Spore Trap and a Tauber Trap in a warm temperate climate. How do airborne and deposition pollen samplers reflect the atmospheric dispersal of different pollen types Annual pollen traps reveal the complexity of climatic control on pollen productivity in Europe and the Caucasus. Comparative study of different methods for capturing airborne pollen, and effects of vegetation and meteorological variables. Dustborne and airborne fungal propagules represent a different spectrum of fungi with differing relations to home characteristics. Sampling, extraction and measurement of bacteria, endotoxin, fungi and inflammatory potential of settling indoor dust. Comparative particle recoveries by the retracting Rotorod, rotoslide, and Burkard spore trap sampling in a compact array. Airborne pollen in Bahía Blanca, Argentina: Seasonal distribution of pollen types. Relative efficiencies of the Burkard 7-Day, Rotorod and Burkard Personal samplers for Poaceae and Urticaceae pollen under field conditions. Tracking the potato late blight pathogen in the atmosphere using unmanned aerial vehicles and Lagrangian modeling. Coordinated aerobiological sampling of a plant pathogen in the lower atmosphere using two autonomous unmanned aerial vehicles. An evaluation of the microscopic counting methods of the tape in Hirst-Burkard pollen and spore trap. An evaluation of two methods used for microscopic analysis of airborne fungal spore concentrations from the Burkard Spore Trap. Ambrosia pollen in Tulsa, Oklahoma: Aerobiology, trends, and forecasting model development. New sampler for the collection, sizing, and enumeration of viable airborne particles. Profiles of airborne fungi in buildings and outdoor environments in the United States. Indoor airborne fungal spores, house dampness and associations with environmental factors and respiratory health in children. Indoor airborne fungi and wheeze in the first year of life among a cohort of infants at risk for asthma. Positive-hole correction of multiple-jet impactors for collecting viable microorganisms. Culturability and concentration of indoor and outdoor airborne fungi in six single-family homes. Olea europaea pollen counts and aeroallergen levels predict clinical symptoms in patients allergic to olive pollen. Air sampling filtration media: Collection efficiency for respirable size-selective sampling. Performance of Air-O-Cell, Burkard, and Button samplers for total enumeration of airborne spores. Performance of the Button personal inhalable sampler for the measurement of outdoor aeroallergens. Concentrations of the major birch tree allergen Bet v 1 in pollen and respirable fine particles in the atmosphere. Detection of airborne fungal spores sampled by rotating-arm and Hirsttype spore traps using polymerase chain reaction assays. Immunologic, spectrophotometric and nucleic acid based methods for the detection and quantification of airborne pollen. Biomolecular identification of allergenic pollen: A new perspective for aerobiological monitoring. Molecular approaches for the analysis of airborne pollen: A case study of Juniperus pollen. Assessment of fungal diversity in the environment using metagenomics: A decade in review. Spore dispersal of basidiomycete fungi at the landscape scale is driven by stochastic and deterministic processes and generates variability in plant-fungal interactions. Evaluating multiplexed next-generation sequencing as a method in palynology for mixed pollen samples. Allergenic Pollen: A Review of the Production, Release, Distribution and Health Impacts. Forecasting model of Corylus, Alnus, and Betula pollen concentration levels using spatiotemporal correlation properties of pollen count. An algorithm and a device for counting airborne pollen automatically using laser optics. Automated pollen monitoring system using laser optics for observing seasonal changes in the concentration of total airborne pollen.
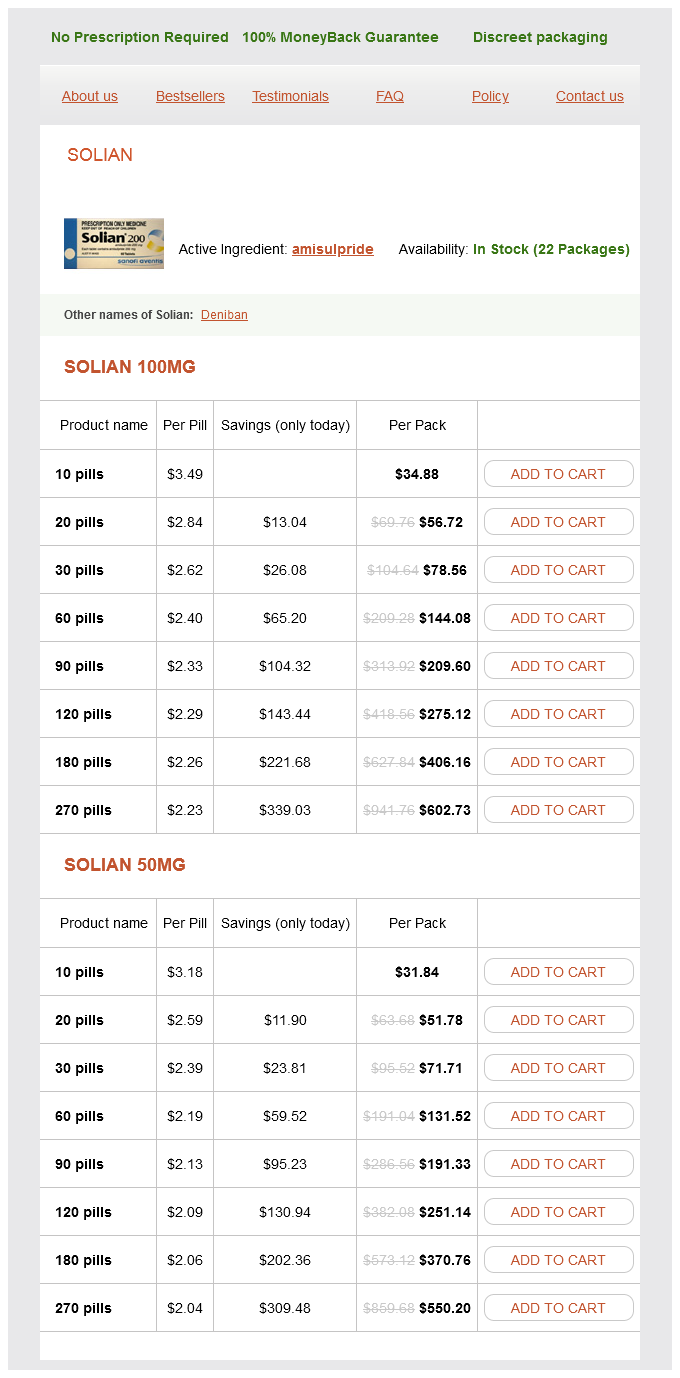
Solian Dosage and Price
Solian 100mg
- 10 pills - $34.88
- 20 pills - $56.72
- 30 pills - $78.56
- 60 pills - $144.08
- 90 pills - $209.60
- 120 pills - $275.12
- 180 pills - $406.16
- 270 pills - $602.73
Solian 50mg
- 10 pills - $31.84
- 20 pills - $51.78
- 30 pills - $71.71
- 60 pills - $131.52
- 90 pills - $191.33
- 120 pills - $251.14
- 180 pills - $370.76
- 270 pills - $550.20
Indications for and preparing and administering subcutaneous allergen vaccines Harold S symptoms of discount solian 50 mg buy online. It is particularly indicated in patients whose symptoms do not respond sufficiently to or who do not tolerate pharmacotherapy. The other approaches to treatment of allergic respiratory disease are allergen avoidance and pharmacotherapy. Avoidance is of limited usefulness for seasonal exposures, but pet, rodent, and cockroach elimination are effective, and the results with house dust mite control measures are favorable in patients with house dust mite sensitization and exposure [3]. The usual first approach to treating allergic respiratory disease is pharmacotherapy. The choice will usually be made by discussion between the physician and the patient. This caution applies to those modified extracts that were not studied, to most fungal extracts, and to cockroach extracts. When polysensitization is accompanied by symptoms to multiple allergens, patients are termed polyallergic. Practice Parameters caution that patients should be treated only with relevant allergens [9]. They recommend that only the most clinically important allergen extract be administered or, if two extracts containing unrelated allergens 26. The odds ratio for not developing asthma in the treated group, compared to the control group, was approximately 2. The inhalant allergen extracts that are currently standardized are house dust mites (Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus and Dermatophagoides farinae), cat hair (which is low in cat serum albumin) and cat pelt (which contains substantial amounts of cat albumin), short ragweed (Ambrosia elatior), and eight grasses (Bermuda, June, meadow fescue, orchard, red top, rye, sweet vernal, and timothy). A second group of standardized extracts are the venoms of the stinging Hymenoptera. These are standardized on the basis of a venom protein content of 100 mcg/mL for all the individual species, or 300 mcg/mL for the mixed vespids. Nonstandardized extracts are available in either a 50% glycerin or an aqueous solution. Glycerin at 50% concentration inhibits microbial growth and maintains the potency of allergenic extracts. Phenol, which is added to aqueous extracts to inhibit bacterial and fungal growth, has an adverse effect on the potency of stored extracts. The choice between the two extracting and diluting fluids would favor glycerin were it not for the discomfort associated with injection of 50% glycerin [22]. A limited number of pollen extracts are available adsorbed to aluminum to delay their absorption from the injection site. In the United States, allergen extracts are either standardized or nonstandardized and are available in a variety of formulations: lyophilized, adsorbed to aluminum, or as aqueous or 50% glycerin solutions. Neither provides precise information regarding the allergenic potency of the extract. However, it is likely that within broad limits many extracts obtained from the same commercial supplier have reasonable reproducible batch-to-batch potency [25]. Thus, it is possible, as a general practice, to refill allergy treatment vaccines with new lots of the same stated potency from the same manufacturer without untoward reactions by reducing the first injection from the new vial by approximately one-third to one-half of the previous dose. Weight by volume (w/v) is the simplest way to express the potency of allergen extracts. It is only necessary to weigh the material to be extracted and measure the volume of extracting fluid. Thus, 10 g of pollen extracted in 100 mL of extracting solution yields a final concentration of 1:10 w/v. One advantage of this method of expressing potency is that the extract need not be further diluted to achieve the desired level of potency. First, the protein nitrogen content is determined, and then the content is converted to units (one unit equal to 0. The major allergens usually represent only a few percent of the total protein content of allergen extracts. In contrast, the extracts of cat and short ragweed 384 Indications for and preparing and administering subcutaneous allergen vaccines extracts are commercially available in specific concentrations. The potency of the grasses and house dusts mites is based on quantitative intradermal skin testing. Therefore, the investigators conclude that a maintenance dose containing 7 µg Der p I/injection appears to be optimal based on benefit/risk considerations. Olsen treated 23 adult subjects with asthma for 1 year with a maintenance dose of 7. Compared to subjects who received placebo, those treated with mite vaccines had significantly decreased symptoms of asthma and required less -adrenergic agonists and inhaled corticosteroids. Ewbank [34] compared the clinical response shortly after achieving maintenance doses, by a cluster buildup, of vaccines containing 0. This study was duplicated in 28 additional catallergic subjects, and outcomes were assessed both after reaching maintenance and again after 1 year of maintenance injections [35]. Catspecific IgG4 was significantly increased with the two higher doses, but only the dose containing 15 µg/injection of Fel d 1 produced sustained reduction in symptoms on nasal challenge. The conclusion of these two studies is that a maintenance dose of cat vaccine containing 15 µg of Fel d 1 is superior to one containing 3 µg of Fel d 1, while the results with a maintenance dose containing only 0. There are a number of randomized, double-blind studies in which the effective dose is expressed in terms of the major allergen administered at maintenance (Table 26. In some instances, only one concentration was employed, but the clinical benefit was demonstrable within a few months to a year and was clinically relevant. In other studies, more than one dose was employed so, for those vaccines, both an effective and a suboptimal dose have been defined (Table 26.