General Information about Diabecon
Diabetes is a chronic condition that impacts tens of millions of people worldwide. It is a disease characterised by excessive levels of blood sugar, which can lead to quite a few issues if left uncontrolled. For many years, pharmaceutical corporations have been developing medications to assist handle diabetes. However, these drugs can include a number of side effects, making it challenging for patients to stick to their remedy plans. This is where Diabecon, an ayurvedic formulation comes into the picture, providing a extra natural and safer method to glycemic control.
Diabecon is an ayurvedic blend of over 30 herbs and minerals particularly designed to assist manage diabetes. Developed by Himalaya Drug Company, a pioneer within the field of natural healthcare, Diabecon is a result of in depth research and scientific trials. It is known to enhance insulin function, regenerate pancreatic beta cells, and cut back oxidative stress, all of which are essential in managing diabetes.
Another necessary herb in Diabecon is bitter melon, also known as Momordica charantia. Bitter melon has been discovered to have anti-diabetic properties, with research displaying its effectiveness in decreasing blood sugar ranges. It can also be known to improve insulin sensitivity, making it simpler for the physique to make the most of glucose. Bitter melon additionally helps reduce inflammation, which is a contributing factor to the event of sort 2 diabetes.
One of the vital thing components in Diabecon is Gymnema sylvestre. This herb has been used in Ayurveda for tons of of years to manage diabetes. It is thought to have a “sugar blocking” impact, preventing the absorption of sugar in the intestine and lowering post-meal glucose levels. Gymnema also helps regenerate the beta cells within the pancreas, that are responsible for producing insulin, thereby enhancing the body's ability to use glucose effectively.
Diabecon additionally accommodates herbs similar to Indian gooseberry, Indian Kino Tree, Guggul, Tribulus, and Haritaki, all recognized for their anti-diabetic properties. These herbs work together to assist manage blood sugar ranges, cut back the danger of diabetes-related problems similar to nerve harm and improve general well being.
Fenugreek, a commonly used spice in Indian delicacies, is also a key ingredient in Diabecon. It has been found to have a hypoglycemic effect, that means it helps lower blood sugar ranges. Fenugreek also accommodates fiber, which slows down the absorption of carbohydrates within the physique, preventing spikes in blood sugar ranges after meals. Additionally, fenugreek has been discovered to enhance insulin sensitivity and scale back insulin resistance.
Unlike many conventional diabetes medications, Diabecon has minimal unwanted effects. This is as a end result of it is created from natural elements and does not include any synthetic chemicals. Patients can take Diabecon with out the concern of growing antagonistic reactions similar to stomach upset, weight achieve, or hypoglycemia.
Another significant advantage of Diabecon is its affordability. Diabetes medications may be expensive, and not everyone can afford them, particularly in growing nations where diabetes is on the rise. Diabecon offers another for many who are unable to entry typical drugs or those who favor pure remedies.
In conclusion, Diabecon is an ayurvedic mix of herbs and minerals that gives a gentle and secure approach to controlling blood sugar levels. It not solely helps manage diabetes but in addition improves insulin function, reduces oxidative stress, and prevents issues related to the disease. With minimal unwanted side effects and affordability, Diabecon is a promising possibility for people on the lookout for a pure and holistic approach to managing diabetes. However, it is all the time advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication, including herbal cures corresponding to Diabecon.
Few data support the accuracy of plain films in detecting or evaluating treatment for constipation (Reuchlin-Vroklage et al blood glucose vs csf glucose buy generic diabecon pills, 2005; Berger et al, 2012). A and B, Images of the kidneys demonstrate echogenic renal parenchyma, moderate to severe hydronephrosis, and renal cortical cyst (upper pole left kidney). In the setting of disorders of sexual differentiation, sonography and urogenitography are typically the only studies needed for diagnosis and surgical planning. Doppler sonography (A) shows the "whirlpool" sign, which has been associated with torsion of the spermatic cord. This advantage is best realized in cases of blunt abdominal trauma and polytrauma. Similar to ultrasonography, it is a detailed anatomic study but with the ability to imply function in noncalcareous hydronephrosis with the addition of intravenous contrast medium and delayed images. Although a delayed nephrogram and ureteral drainage compared with the contralateral side signals obstruction, this is difficult to quantitate. Genitalia Urogenitography can provide essential information for surgical planning and classification of patients with disorders of sexual differentiation. Typically, a catheter is placed within the single perineal opening, and contrast medium is injected under fluoroscopy to identify the confluence of urethral and vaginal structures as well as their orientation. Alternatively, a Foley catheter can be used with the balloon inflated and pressed up to the perineum with the tip in the perineal opening for retrograde filling (Chavhan et al, 2008). A,Sonogramofthekidneyswith Doppler views demonstrates a heterogeneous collection in the lower pole of the left kidney. Complete filling of the bladder with contrast medium is necessary to avoid missing small leaks secondary to insufficient intraluminal pressure or gravitational settling of contrast medium on the opposite side of the perforation. Diuretic Scintigraphy the gold standard for differentiation of obstructive and nonobstructive hydronephrosis and hydroureter is diuretic renography. A strict protocol should be followed to ensure accurate and reproducible results (Majd, 1989; Conway and Maizels, 1992; Shulkin et al, 2008). The clinician should review the actual drainage images, regions of interest used, and curves because any variation in technique can lead to misleading results. There are three key elements to successful diuretic renography: hydration, bladder drainage, and timing of diuretic administration. Ideally, an intravenous line is placed for hydration before the study in addition to encouragement of oral hydration before arrival for the study. Poor hydration or poor renal function can lead to false-positive results owing to a slow uptake curve and poor diuretic response. Intravenous furosemide (1 mg/kg) is ideally given when the dilated collecting system is determined to be maximally filled; however, timing of diuretic administration is largely institution specific. Other common protocols give the diuretic 20 minutes after injection of the tracer (F+20), right after the tracer (F+0), or 15 minutes before the tracer (F-15). Although acute pyelonephritic lesions appear as areas of decreased peripheral uptake with preservation of the reniform contour, renal scars can be differentiated based on observation of volume loss, which interrupts the normal reniform outline, resulting in a concavity. Although it is possible for an experienced observer to distinguish between acute and chronic lesions, differentiation is frequently difficult in kidneys with acute pyelonephritis superimposed on preexisting renal scars. A similar experiment demonstrated slightly higher sensitivity with lower specificity but equivalent diagnostic accuracy when using single photon emission computed tomography detection compared to planar (pinhole) detection (Majd et al, 1996). A, Renal sonogram demonstrating grade 3 hydronephrosis (mostly intrarenal dilation)withouthydroureter. Tempered" approach, it requires active participation of an experienced technician or radiologist (Conway and Maizels, 1992). The F+0 approach has shown reliable results in children with less experience needed, but it may be more difficult to interpret in slow-filling, capacious collecting systems (Wong et al, 1999). It is important to know which protocol is being used to interpret the test accurately and/or compare with previous studies. During the diuretic phase, the region of interest should be drawn around the collecting system, including the ureter only in cases of hydroureter. After completion of the diuretic phase recording, the child should be held upright for 5 minutes and allowed to void if no catheter was used. A repeat image is captured to assess residual activity after gravity-assisted drainage. Differential renal function, washout curves, and washout half-times can be computer-generated for proper interpretation of the test (Shalaby-Rana et al, 1997). Management decisions are based on renal function, radiotracer washout half-time, shape of the washout curve, and gravity-assisted drainage. In contrast to adults, in children there are no established washout half-times that define an obstructed or unobstructed state. The washout curve is typically more revealing than the absolute half-time values, especially in young children or children after pyeloplasty in whom a dilated system may be slow to drain but not obstructed. In cases of equivocal washout curves, gravityassisted drainage of less than 50% residual activity can be used to confirm obstruction (Wong et al, 2000). All the information acquired from the scan must be used to determine the proper management instead of one parameter in isolation. In this example, three consecutive 99mTcmercaptoacetyltriglycine diuresis renograms on the same patient demonstrate progressively poor drainage (prolongation of the halftime[T 12]andretentionoftracer). However, it lacks the anatomic resolution of the collecting system and urethra, still requires urethral catheterization, and is still a nonphysiologic measurement. However, its lack of availability, invasiveness, and radiation Radionuclide Testicular Scanning Testicular scintigraphy has been around since the 1970s and is typically promoted to distinguish between testicular torsion and inflammatory conditions of the testicle. The test is performed by intravenous injection of 99mTc pertechnetate followed by dynamic and static gamma images of the pelvis.
For all these reasons gestational diabetes definition who generic diabecon 60 caps buy on line, the severity of damage is often unclear and management defaults to preserving remaining function, avoidance of additional insults, supportive care, and watchful waiting. Furosemide and "renal dose" dopamine have been shown not to be effective in improving outcomes, although urine output may increase and maintenance of effective perfusion pressure is essential. Likewise, N-acetylcysteine, fluids, sodium bicarbonate, statins, fenoldopam, and theophylline have all failed to show consistent benefits as treatment options. Hopefully, improved diagnosis, including the use of early and more specific biomarkers, and better understanding of the bimodal effects of some treatments. Hyperkalemia develops from decreased filtration, acidosis, tissue damage, and catabolism. Acidosis develops from impaired secretion of normal acid production, increased acid production resulting from ischemia and catabolism, and compromise of respiratory compensation in the critically ill. Hypocalcemia and hyperphosphatemia are also common and require attention to nutritional support. Modality choice is most often based on center experience and preference (Sutherland et al, 2014). Approximately 7500 children were receiving dialysis or had functioning renal transplants in 2012 (United States Renal Data System, 2014c). Management Current treatment strategies should include restoration of adequate renal blood flow and avoidance of nephrotoxic drugs. Fluids should be given to restore intravascular volume with the reminder that aggressive fluid administration without careful attention to cardiovascular responses risks the morbidity and mortality induced by fluid overload-risks that appear with as little as 10% excess fluid (Foland et al, 2004). It is important to note that this classification does not officially apply to children less than 2 years of age who have not yet reached normal renal functional maturity, and the system applies to patients with kidney disease for greater than 3 months. Stages 1 and 2 require evidence of kidney damage, defined as structural (on biopsy) or functional (proteinuria, hypertension, or abnormal imaging). In the case of congenital anatomic disorders, intervention should be considered to ensure regular voiding, maintain adequate drainage of the urinary tract, and prevent infection. Medical management can delay the development and effects of metabolic disarray but is rarely effective in halting the process completely (Wong et al, 2012; Massengill and Ferris, 2014). Children with cystic dysplasia, obstructive uropathies, and tubulopathies exhibit disrupted renal concentrating capacity and may require sodium and water supplementation and special attention during times of acute illness that risk dehydration. In contrast, children with chronic glomerulonephritis may need salt and water restriction to prevent edema and hypertension. If uncorrected, chronic acidosis results in retardation of linear growth as well as decreased bone mineralization. Oral alkali therapy (with bicarbonate, acetate, or citrate) corrects the abnormalities. Aluminum salts are no longer used because of complications of neurotoxicity with long-term use. Treatment requires restoration of normal iron stores and parenteral (commonly subcutaneous) erythropoiesis-stimulating agents. Both short-acting recombinant erythropoietin and longer-acting glycosylated forms are in current use. Poor appetite, limited food options, and oromotor dysfunction all contribute to impaired nutrition and poor linear growth. However, growth delay is closely associated with neurocognitive delays in development, and aggressive maintenance of necessary nutrition is imperative for long-term outcomes. Enteral feeding may be used at night in order to maintain normal social eating behavior patterns while supplementing needed calories for growth. Short stature results from poor nutrition, renal osteodystrophy, electrolyte imbalance, and derangements in the growth hormoneinsulin-like growth factor-1 axis. Once adequate caloric intake is established, treatment with recombinant human growth hormone is indicated if the height standard deviation score is less than -2. Unfortunately, a number of barriers continue to disincentivize growth hormone use, including daily subcutaneous injections, high cost, and cultural factors. Therefore hypertension should be treated with goals at or below the 90th percentile for age, sex, and height. Patients with pulmonary, cardiac, or liver disease or with solidorgan/stem cell transplants have poorer outcomes (mortality rates of 49% to 69%), whereas those with renal disease, inborn errors of metabolism, and tumor lysis fare better (mortality rates of 16% to 27%) (Sutherland et al, 2014). This section reviews the indications, limitations, and necessary processes for each modality. Intracapillary perfusion pressure within the membrane is quite low, but in the absence of abdominal compartment syndrome it will be higher than intra-abdominal pressure, and exchange occurs freely. Standard dialysate solutions are designed to remove sodium, potassium, urea, and phosphorus and deliver calcium and base equivalents (acetate or lactate) that are subsequently converted to bicarbonate. Custom-made dialysate solutions may be designed and made by hospital pharmacies for short-term use in unusual situations. Acute infection and recent abdominal surgeries are relative contraindications given the unlikely nature of resolving infection with an indwelling catheter and the potential for leakage through recent incisions. The outcomes of the two groups in terms of length of stay, complications, and survival to discharge were not different. The most effective peritoneal catheter placement is surgical, with generation of a subcutaneous tunnel that decreases the risk of infection, dislodgement, and leak. Short-term use of an "acute" catheter placed with local anesthesia and the Seldinger technique is now rare because effective bedside anesthesia is now routine in the units that would offer these technologies. For chronic dialysis, the most important decision point is actually the choice of modality (Schaefer and Warady, 2011; Warady et al, 2014).
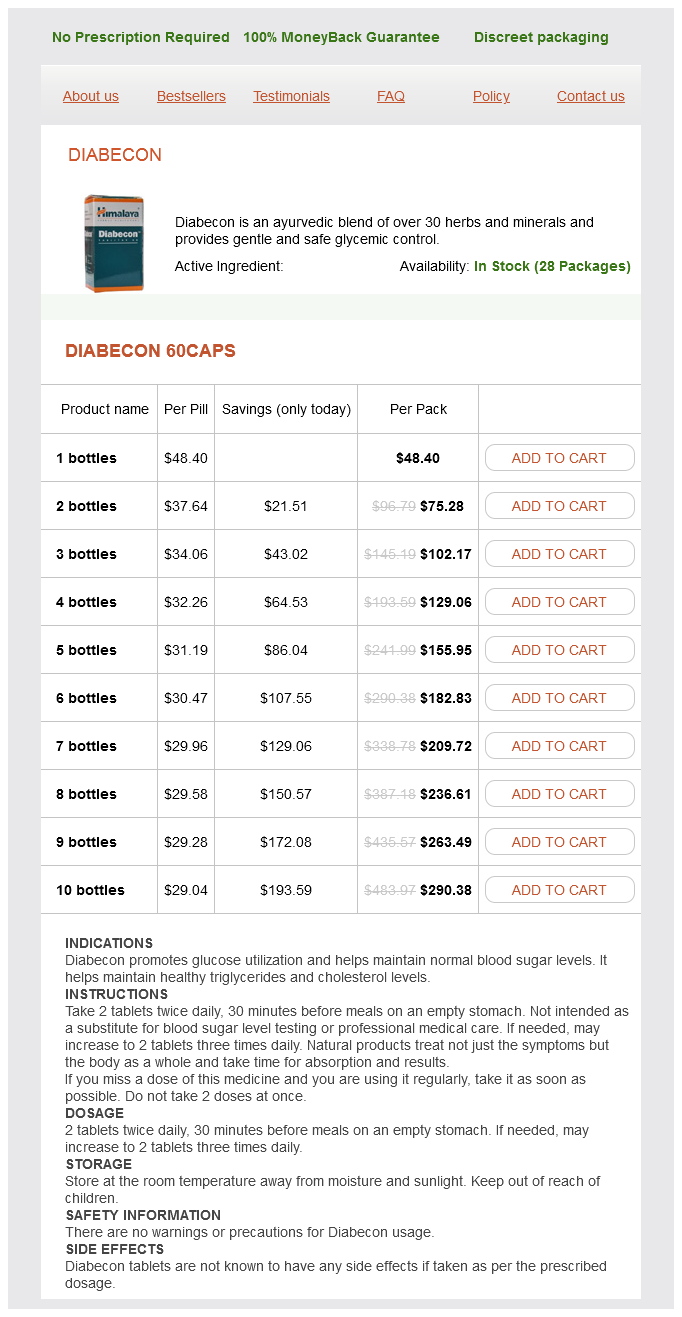
Diabecon Dosage and Price
Diabecon 60caps
- 1 bottles - $48.40
- 2 bottles - $75.28
- 3 bottles - $102.17
- 4 bottles - $129.06
- 5 bottles - $155.95
- 6 bottles - $182.83
- 7 bottles - $209.72
- 8 bottles - $236.61
- 9 bottles - $263.49
- 10 bottles - $290.38
Acetazolamide (Diamox)1 125 to 250 mg bid or furosemide (Lasix)1 10 to 20 mg daily are also options diabetes y sus complicaciones buy diabecon line. Patients with severe sulfa allergy can use low-dose ethacrynic acid (Edecrin)1 12. Scopolamine in patch form (Transderm-Scop)1 is too slow to be useful because ¯ it takes hours to be absorbed transdermally; oral scopolamine tablets (Scopace)1 0. Nausea can additionally be managed with prochlorperazine (Compazine) 10 mg orally or 25 mg by suppository, with oral or sublingual ondansetron (Zofran)1 4 to 8 mg, or with other antiemetics. The role of betahistine is not firmly established, although it is widely prescribed for vertigo throughout the world. Betahistine may be helpful when successful medical management with diet and diuretics has helped but is inadequate to stop attacks. Betahistine is a vasodilator, a modest H1 histamine agonist, and a powerful H3 histamine receptor antagonist. It is available outside the United States in the form of Serc (Solvay Pharmaceuticals, Belgium). Betahistine may be made within the United States at compounding pharmacies with a physician prescription and may also be imported from outside the United States for individual use. Betahistine is not histamine, and we have not found it to cause or aggravate urticaria. Such triggers should be avoided when possible, but strong associations with these triggers can also occur in migrainous vertigo. It is presumed that if attacks of vertigo, ear fullness, fluctuating hearing, and tinnitus are all stopped, hearing should stabilize, but this is still a supposition. When a patient has very frequent vertigo attacks and is disabled, more-aggressive treatment may be considered sooner. The possibility of bilateral involvement weighs on the decision making for any procedures that sacrifice hearing or vestibular function because it leaves the patient with only one functioning labyrinth. Serviceability of Hearing Serviceable hearing is residual hearing that can be useful to the patient by wearing hearing aids. In general, because hearing loss is permanent, one should avoid sacrificing any serviceable hearing. If spells are infrequent, symptomatic management of vertigo attacks may be the best option. Gentamicin is a commonly used aminoglycoside antimicrobial agent with activity against gram-negative bacteria that also happens to be ototoxic. It damages hair cells of the labyrinth and preferentially affects hair cells of the vestibular neuroepithelium over that of the cochlea. Even so, transtympanic administration still has some risk of causing hearing loss. To avoid rapid drainage through the eustachian tube, the injection is done with the patient supine and kept in that position for an hour or so to allow the gentamicin to absorb through the round window into the inner ear. There are many protocols, but commonly an injection is given once, and additional injections can be considered every 3 to 4 weeks until improvement in vertigo attacks is realized. Intratympanic Steroids Sometimes, a trial of intratympanic corticosteroids may be tried, though its effectiveness in controlled trials is still not compelling. Even so, a trial of corticosteroids administered in this manner poses little risk. This procedure involves craniotomy and severing the vestibular nerve while preserving the cochlear nerve. This procedure requires overnight hospitalization and general anesthesia, and it does pose some risk to facial nerve function and hearing on the affected side. This procedure entails the removal of the membranous labyrinth and is highly effective in stopping recurrent vertigo attacks from that ear. In elderly patients or those who are poor surgical candidates, a more limited transtympanic cochleosacculotomy may be performed. Meniett Treatment the Meniett device is a portable low-frequency pressure-wave delivery system that administers a wave of pressure of about 12 cm H2O to the middle ear via a tympanostomy tube for about 0. Quality randomized trials demonstrating the effectiveness of this treatment are very limited, however. This method has few risks and only requires myringotomy and a pressure equalization tube. A practical limitation is the cost of the device, which is not often paid for by many health insurance companies. Endolymphatic Sac Surgery Another option for patients with residual functional hearing is endolymphatic sac shunt or decompression. Periodic audiometry is probably the most sensitive measure of stabilization of the condition. Vestibular testing may be considered when changes might alter the treatment strategy. It is a common problem in primary care, with an annual incidence of about 1% and lifetime incidence of about 10%. Trauma to the external canal (such as selfinflicted injury with a cotton swab) is also a risk factor. Genetic factors may play a role, and people with narrow external canals or absence of ear wax are at increased risk.