General Information about Ayurslim
In conclusion, AyurSlim is a researched ayurvedic herbal product that has gained a popularity for its favorable impact on weight reduction and lipid profiles. It is a protected and natural alternative to traditional weight loss dietary supplements, with no identified unwanted side effects. With regular use, AyurSlim can assist people in reaching their weight loss objectives and lead a healthier life.
Another essential ingredient in AyurSlim is Gymnema Sylvestre, also recognized as 'Gurmar' in Ayurveda, which suggests 'destroyer of sugar'. This herb helps to manage blood sugar levels, thereby decreasing cravings for candy and sugary meals. It additionally has a constructive impact on levels of cholesterol, which is important for maintaining a wholesome weight.
Ayurveda, the ancient Indian system of drugs, has gained reputation over the years for its holistic approach to therapeutic and maintaining a healthy way of life. One of essentially the most generally used Ayurvedic natural products for weight administration is AyurSlim.
AyurSlim also contains Indian Bdellium, which helps in decreasing cholesterol and triglyceride levels. This herb has also been found to have a big impression on lowering body fat and growing metabolism.
What units AyurSlim other than other weight management supplements on the market is that it's not only a fat burner. It focuses on an general enchancment within the physique's functioning, which contributes to weight reduction in the long term. This herbal product doesn't declare to supply quick fixes or miraculous results, but a gradual and sustained weight loss.
The mixture of those natural herbs in AyurSlim works together to spice up weight loss by decreasing urge for food, inhibiting fats manufacturing, and regulating the body's metabolism. Additionally, it also has a helpful effect on lipid profiles by decreasing levels of ldl cholesterol and triglycerides.
Another advantage of utilizing AyurSlim is that it is straightforward to include into one's every day routine. It comes within the form of capsules, making it handy to devour with a glass of water, ideally earlier than meals. The really helpful dosage is 2 capsules twice a day, making it easy for individuals to observe the recommended regimen.
AyurSlim is a researched, pure supplement that aids in weight discount and improves lipid profiles. It is a mix of natural herbs which were fastidiously chosen and blended to target weight reduction in a secure and effective manner. This herbal product is manufactured by the renowned Himalaya Drug Company, which has been in the enterprise of producing pure and efficient healthcare products for many years.
The major component of AyurSlim is Garcinia Cambogia, a small fruit native to Southeast Asia and India. This fruit has been used in Ayurveda for lots of of years to aid in digestion and weight administration. It is rich in Hydroxycitric acid (HCA), which acts as a natural appetite suppressant and inhibits the manufacturing of fats within the body.
One of the major issues that folks have with weight loss dietary supplements is the potential side effects. However, AyurSlim is a one hundred pc natural and secure natural product with no identified unwanted facet effects. It is appropriate for long-term use as it does not contain any harmful chemical compounds or components.
AyurSlim isn't just a weight management supplement but a holistic strategy to main a wholesome life-style. It has been clinically examined and proven to be efficient in aiding weight loss and bettering lipid profiles. However, it's important to notice that AyurSlim must be used in conjunction with a healthy diet and regular exercise for optimal outcomes.
The most common presenting symptoms are weakness/paresis herbals for blood pressure purchase cheapest ayurslim and ayurslim, pain, and sensory changes. In addition to the location of the tumor in the spinal cord, presenting signs also depend on whether the tumor is intramedullary, intradural-extramedullary, or extramedullary. Spinal cord oligodendroglioma with 1p and 19q deletions presenting with cerebral oligodendrogliomatosis. Intramedullary tumors of the spinal cord: a review of fifty-one cases, with an attempt at histologic classification. A very rare spinal cord tumor primary spinal oligodendroglioma: a review of sixty cases in the literature. Primary spinal cord oligodendroglioma with postoperative adjuvant radiotherapy: a case report. Spinal cord anaplastic oligodendroglioma with 1p deletion: report of a relapsing case treated with temozolomide. Thirty-one-year cure following removal of intramedullary glioma of cervical portion of spinal cord: report of case. Untersuchungen zur Statistik der Biologie und Pathologie Intrakranieller und Spinaler Raumfordernder Prozesse. Raised intracranial pressure due to spinal tumours: 3 rare cases with a probable common mechanism. Thoracolumbar intraspinal tumours presenting features of raised intracranial pressure. Primary spinal cord oligodendroglioma: a case report and review of the literature. Isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 mutations: a fundamentally new understanding of diffuse glioma As of 2018 to our knowledge only four confirmed cases were reported in the literature. This case was a 52year-old man who presented with signs of retinal detachment that included six months of deteriorating vision associated with metamorphopsia. The authors report that ciliary retinal stems cells have "the same properties of mobility and pluripotentiality as neural stem cells. A 3-year-old boy presented with new onset of headaches, fever, nausea, and vomiting with a longstanding history of right esotropia since the age of 6 months. Initially, he was thought to have heat stroke, but when the headaches reoccurred he was hospitalized and ophthalmology saw the patient. Examination revealed a large mass above and temporal to the right optic disc; ultimately, he required enucleation due to probable retinoblastoma. Per report, neurological examination was essentially unremarkable except for nystagmus on lateral gaze. However, the permanent sections were more consistent with a high-grade glioneuronal tumor. Given the complexity of the case, the tissue was sent out for further pathological evaluation. The patient underwent neuropsychiatric testing that revealed attention dysfunction and a delayed rate of information processing in the immediate postoperative phase, but the patient ultimately did return to neurological baseline. She underwent total excision of the tumor via midline infratentorial supracerebellar approach to the pineal region. Given that the tissue was almost exhausted during immunohistochemistry an attempt was made to test for 1p and 19q, which did not show deletion. A shunt was placed urgently with no improvement in her visual symptoms, and she then underwent a supracerebellar infratentorial approach for tumor resection. He underwent biopsy of the tumor; the neoplastic cells had round nuclei with a moderate degree of pleomorphism and were surrounded by a perinuclear halo. One was lost after 1 month, and the other had been followed for a year at the time of publication. The radiotherapy dosage was not provided in the publication and they reported that at one-year follow up he was tumor free. On examination she was found to have ataxia, cerebellar syndrome, left sixth nerve palsy, and papilledema. The patient then underwent tumor debulking and did well with no change in deficits, except for minor exacerbation of right-sided motor weakness. The authors state their case was distinctive because there was invasion of the midbrain from tumor in the pontine tegmentum. A biopsy was performed and on histological examination demonstrated highly cellular anaplastic oligodendroglial cells with perinuclear halos. The tumor was screened for the presence of K27 M or G34 V mutations in histone H3. On examination, she had findings of hemifacial palsy, right-sided dysmetria, dysdiadochokinesia, and wide-based gait. Imaging studies revealed a cyst-like, heterogeneous, hyperintense, welldemarcated lesion located in the right cerebellar peduncle. The case was that of a 10-year-old boy who was admitted with persistent nausea and emesis. These patients received radiation and chemotherapy with radiation, respectively, and survived 57.
At terminal flexion lotus herbals 3 in 1 safe ayurslim 60 caps, the sacrotuberous ligaments become taut and the sacral base will move posteriorly. As weight bearing shifts from one side to the other while walking, the sacrum engages two sacral oblique axes. Weight bearing on the left leg (stepping forward with the right leg) will cause a left sacral axis to be engaged. Innominate dysfunction (Remember, the side of the positive standing flexion test is the side of the dysfunction. Posterior innominate rotation One innominate will rotate posteriorly compared to the other. Etiology: It can be due to a fall on the ipsilateral buttock or a mis-step Static finding: 1 p. Superior pubic shear A condition where one pubic bone is displaced superiorly compared to the other. Inferior pubic shear A condition where one pubic bone is displaced inferiorly compared to the other. Innominate inflares A condition where the innominate will rotate medially around a vertical axis. Therefore the distance between the A518 and umbilicus is less than that of the contralateral side. Innominate outflare A condition where the innominate will rotate laterally around a vertical axis. Somatic dysfunctions of the Sacrum There are two models to describe sacral dysfunction. Anterior sacrum - the left or right sacral base will rotate forward and sidebend to the opposite side of rotation. The movement of the sacrum is about an oblique axis and the findings are very similar to a forward sacral torsion (see below). Posterior sacrum - the left or right sacral base will rotate backward and sidebend to the opposite of the rotation. The movement of the sacrum is about an oblique axis and the findings are very similar to a backward sacral torsion (see below). Definition - Sacral rotation about an oblique axis along with somatic dysfimction at L5. Sacral torsion rules - Due to lumbosacral biomechanics, if a sacral torsion is present, certain reproducible L5 and seated flexion test findings are produced. Rule #1: When L5 is sidebent, a sacral oblique axis is engaged on the same side as the sidebending. Rule #2: When L5 is rotated, the sacrum rotates the opposite way on an oblique axis. Rule #3: the seatedflexion test is found on the opposite side of the oblique axis. Palpatory model for sacral torsions 1° Springing over sacral landmarks in sacral torsions - Springing (motion) present over the part of the sacrum that moved anterior. Forward sacral torsion In a forward sacral torsion, rotation is on the same side of the axis. Backward sacral torsion In a backward sacral torsion, rotation is on the opposite side of the axis. Bilateral sacral flexion (sacral base anterior) In this somatic dysfunction, the entire sacral base moves anterior about a middle transverse axis. Bilateral sacral extensions (sacral base posterior) In this somatic dysfunction, the entire sacral base moves posterior about a middle transverse axis. However, it is mentioned here because this dysfunction is taught at some osteopathic institutions. In a sacral margin posterior, the sacrum rotates posteriorly about a midvertical or parasagittal vertical axis. Anterior and posterior sacrum - these models were originally described by Strachan in 1938. These somatic dysfunctions describe sacral motion in relation to the ilium (as opposed to the Mitchell model which describes sacral motion in relation to L5). Anterior Sacrum In an anterior sacrum left, the left sacral sulcus has moved anterior around an oblique axis. Short leg mdrome/ postural imbalances A chronic anterior sacrum (or forward torsion) on the side of the short leg is a classic finding. Pubic and pelvic floor dysfunctions Improved pubic motion will allow the ilium to move freely Pubic dysfunction is associated with pelvic floor dysfunction 95 Chapter 6 Sacrum and Innominates 7. Iliolumbar ligament tenderness is often associated with lumbosacral decompensation. Sequencing lumbar-sacrum-pelvis treatment It is generally accepted to treat the lumbar spine, psoas, iluim and pubes before treating the sacrum. A middle-aged adult present with right hip pain and is determined to have an anterior innominate rotation. A 32-year-old female presents with sacroiliac pain that started 2 days ago after lifting her son. Structural examination reveals the sacral sulci are shallow with a positive lumbosacral spring test. The most likely diagnosis is a bilateral sacral flexion on a middle transverse axis flexion on a superior transverse axis flexion on an inferior transverse axis extension on a middle transverse axis extension on an inferior transverse axis 97 Chapter 6 Sacrum and Innominates 4. A 25-year-old male reports right-sided low back and sacroiliac pain 1 week after a prolonged period of sitting. A 30-year-old runner presents with left-sided hip pain that started yesterday after a 5 mile run. A 32-year-old female presents with sacroiliac pain that started 2 days ago after picking up her 3-year-old son.
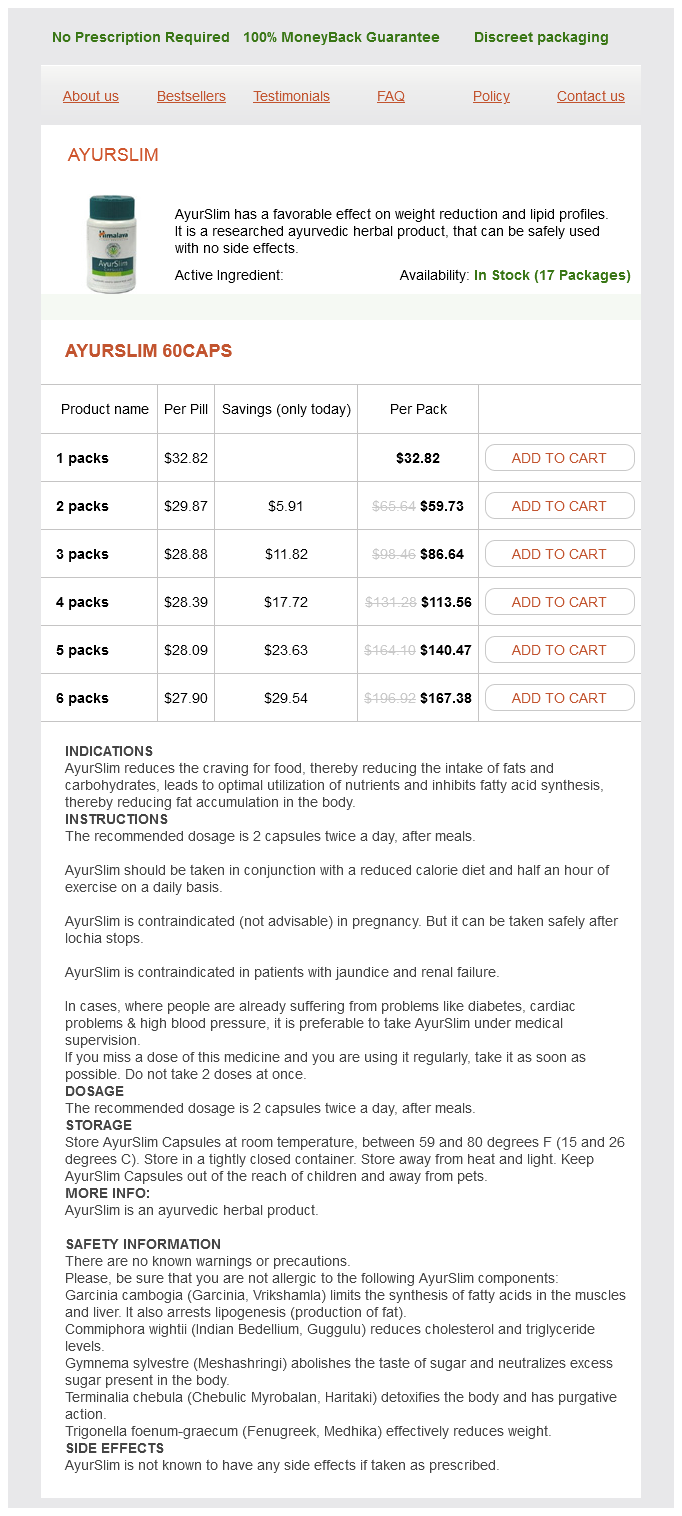
Ayurslim Dosage and Price
Ayurslim 60caps
- 1 packs - $32.82
- 2 packs - $59.73
- 3 packs - $86.64
- 4 packs - $113.56
- 5 packs - $140.47
- 6 packs - $167.38
Answer: C In spina bifida meningomyelocele the lamina defect is usually large and allows the spinal cord (myelo-) to protrude through the defect as opposed to the meninges alone herbal medicine order 60 caps ayurslim with amex. In spina bifida occulta, the only physical sign is a course patch of hair over the site. In spina bifida meningocele, there is a herniation through the lamina defect; however the sac would not contain any neural elements. It is commonly caused by a growing malignant neoplasm but may also be caused by lumbar spinal stenosis from a vertebral body due to a spondylolisthesis, a compression fracture or a severe disc herniation. In adults, the tip of the spinal cord (conus medullaris) usually lies at the L1 vertebral level. The cauda equina is the bundle of nerves and spinal roots below this level, and compression of these structures results in the symptoms mentioned in the stem and explanation below. Note that hyperreflexia is typically more common with lesions above the cauda equina, which is the main reason that distractor A is incorrect. Epidural venous plexus congestion can be due to inferior vena cava occlusion, this has not been associated with decreased rectal tone. Meningeal inflammation and severe spondylolysis will not present with the above neurological deficits. Answer: A In patients with spinal stenosis, symptoms are often worsened with standing and walking. Therefore any structure causing stenosis can result in neural compression with standing and walking. Although weakness in the hip girdle could arise from an upper lumbar stenosis, stenosis in the lower lumbar segments is much more common. The L1 is rotated right because it has resistance with left rotation as noted when applying anterior pressure to the right transverse process. Answer: D Psoas syndrome is due to a psoas spasm that can cause a persistent strain across the lumbosacral junction and is associated with a constellation of signs and symptoms. The pelvic side shift test, like all somatic dysfunctions, is named positive to the side of freer motion. In a contracted psoas on the left, the pelvis will shift to the right, resulting in a positive pelvic shift test to the right. Psoas syndrome is also associated with an L1 or L2 somatic dysfunction (not necessarily L5). Although some authors reported a sacral dysfunction on an oblique axis associated with psoas syndrome, 3 P747 sacral shear and posterior sacrum have not been reported. Other signs include flexed posture sidebent to the affected side, a positive Thomas test, enhanced lumbar lordosis, and tenderpoints of the ipsilateral iliacus and contralateral piriformis. This can be due to bilateral defects of the posterior arch (pars interarticularis) or related to degeneration of the facet joints. Answer: E Spondylosis is a general term for nonspecific, degenerative changes of the spine. Answer: D Spondylolysis is a unilateral or bilateral defect (fracture or separation) in the vertebral pars interarticularis, without anterior displacement of the vertebrae. It is most common in athletes who engage in sports involving extreme spinal motion, particularly lumbar extension. Compression of structures within the intervertebral foramen will compress the L3 nerve root between the L3 and L4 vertebrae. Answer: C the L4 nerve root can be tested by assessing the patellar deep tendon reflex, ankle dorsiflexion, and sensation along the medial leg and malleolus. Depending upon the nature and location of intraspinal compression (central, posteriolateral or lateral), nerve roots may be injured at any disc level, from the L1-2 level where the spinal cord ends as the conus medullaris to the level of their exit into their neural foramina. The L5 root can be compressed by a central disc protrusion at L2-3 or L3-4, a posteriolateral disc protrusion at the L4-5 level, or a lateral disc protrusion into the foramen at L5-Sl. Definition 1) an appreciable lateral deviation of the spine from the normally straight vertical line of the spine. It is associated with vertebral wedging and shortened ligaments and muscles on the concave side of the curve. Screening It is generally recommended that children ages 10 - 15 years old he examined for scoliosis. Scoliosis often increases rapidly during the growth spurt of an adolescent1 "4674* and stabilizes when the patient reaches skeletal maturity. Procedure 1) Examine levelness of occiput, shoulders, iliac crests, posterior superior iliac spines, and greater trochanters. If a rib hump (a group of ribs that appear higher on one side as the patient bends forward) appears, the patient is likely to have scoliosis. Severity of Scoliosis was Severity Mild Cobb angle 5° - 15° Moderate Severe 20° - 45° >500 Respiratoryfunction is compromised if the thoracic curvature is >500. Some patients may have a family history of scoliosis suggesting a genetic component. The goal of conservative treatment is to improve flexibility and strengthen trunk and abdominal musculature. Definition Condition in which there is anatomical or functional leg length discrepancy. Classifications 1) Anatomical leg length discrepancy - one leg anatomically shorter than the other. Signs and Symptoms Although each person with short leg syndrome will compensate differently, certain structural findings can be present. Pelvic side shift to the long leg side Lumbar spine will sidebend away and rotate toward the side of the short leg. If a leg length discrepancy is still present and short leg syndrome is still suspected then: 2) Obtain standing postural x-rays to quantify differences in the heights of the femoral head.